Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
The equation of state (combined gas law) for an ideal gas states that
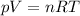
where
p is the gas pressure
V is the volume of the gas
n is the number of moles of the gas
R is the gas constant
T is the absolute temperature of the gas
The equation can be rewritten as
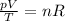
For an ideal gas that undergoes a transformation, if the amount of gas remains the same, the term on the right of the equation remains constant. This means that the ratio
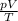
for the gas remains constant, and therefore we can rewrite the equation as

where 1 indicates the initial conditions of the gas while 2 indicates the conditions of the gas after the transformation.