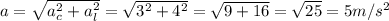Answer:
5 m/s2
Step-by-step explanation:
The total acceleration of the circular motion is made of 2 components: centripetal acceleration and linear acceleration of 4 m/s2. They are perpendicular to each other.
The centripetal acceleration is the ratio of instant velocity squared and the radius of the circle
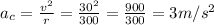
So the magnitude of the total acceleration is