Answer: The molar mass of unknown molecule is 157.07 g/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
The equation used to calculate relative lowering of vapor pressure follows:
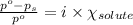
where,
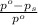 = relative lowering in vapor pressure
= relative lowering in vapor pressure
i = Van't Hoff factor = 1 (for non electrolytes)
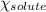 = mole fraction of solute = ?
= mole fraction of solute = ?
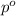 = vapor pressure of pure acetone = 400 torr
= vapor pressure of pure acetone = 400 torr
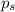 = vapor pressure of solution = 361.8 torr
= vapor pressure of solution = 361.8 torr
Putting values in above equation, we get:
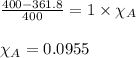
This means that 0.0955 moles of unknown molecule is present in the solution
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
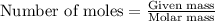
Moles of unknown molecule = 0.0955 moles
Mass of unknown molecule = 15.0 grams
Putting values in above equation, we get:
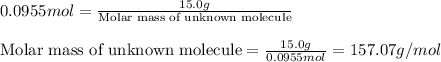
Hence, the molar mass of unknown molecule is 157.07 g/mol