Answer:
Explanation:
Using Bayes' theorem, we have:
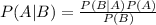
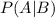 is a conditional probability: the likelihood of event A occurring, given that B is true.
is a conditional probability: the likelihood of event A occurring, given that B is true.
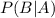 is also a conditional probability: the likelihood of event B occurring, given that A is true.
is also a conditional probability: the likelihood of event B occurring, given that A is true.
P(A) and P(B) are the marginal probabilities of observing A and B, independently of each other.
We solve thus:
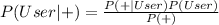
=
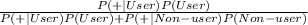
=
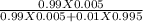
=
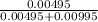
=
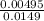
=
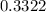 or
or
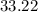 %
%
Therefore, if an individual tests positive, it is more likely than not (1 - 33.2% = 66.8%) that they do not use the drug.