Answer:
Slow down
Step-by-step explanation:
Short wavelengths of visible light interact more frequently with the atoms in glass than do longer wavelengths.
This means that blue light (shorter wavelength) interacts more frequently with the atoms in glass, with respect to red light (longer wavelength).
More interactions, however, means that the speed of the light decreases more. Therefore, blue light is slowed down more than red light.
This can be seen from the formula of the refractive index:
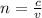
where
c is the speed of light in a vacuum
v is the speed of light in the medium (here, glass)
The index of refraction can also be written as
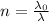
where
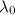 is the wavelength of light in a vacuum
is the wavelength of light in a vacuum
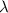 is the wavelength in the medium
is the wavelength in the medium
Therefore, since the two "n" are equals, this means that when light interacts more with the medium, its speed is decreased more, and so light with short wavelength is slowed down more.