Answer:
Kc = 1.54e - 31 / 2.61e - 24
Step-by-step explanation:
1 )
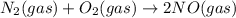 ; Kc = 1.54e - 31
; Kc = 1.54e - 31
2)
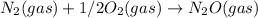 ; Kc = 2.16e - 24
; Kc = 2.16e - 24
upon reversing ( 2 ) equation
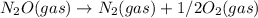 Kc = 1/2.16e - 24
Kc = 1/2.16e - 24
now adding 1 and reversed equation (2)
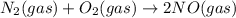
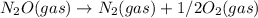
we get ,
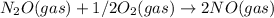 Kc = 1.54e-31 × 1/2.61e - 24
Kc = 1.54e-31 × 1/2.61e - 24
equilibrium constant of equation (3) is -
Kc = 1.54e - 31 / 2.61e - 24