Answer:
The answer to the question is
The rate constant for the reaction is 1.056×10⁻³ M/s
Step-by-step explanation:
To solve the question, e note that
For a zero order reaction, the rate law is given by
[A] = -k×t + [A]₀
This can be represented by the linear equation y = mx + c
Such that y = [A], m which is the gradient is = -k, and the intercept c = [A]₀
Therefore the rate constant k which is the gradient is given by
Gradient =
![([A]_(2) - [A]_(1) )/(t_(2) - t_(1) )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/t8puy3gv1upf400jgkh862f19y7ibqzobh.png) where [A]₁ = 8.10×10⁻² M and [A]₂ = 1.80×10⁻³ M
where [A]₁ = 8.10×10⁻² M and [A]₂ = 1.80×10⁻³ M
=
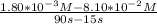 = -0.001056 M/s = -1.056×10⁻³ M/s
= -0.001056 M/s = -1.056×10⁻³ M/s
Threfore k = 1.056×10⁻³ M/s