Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Given
mass of ethanol
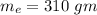
mass of aluminium cup
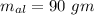
both are at an initial temperature of
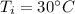
specific heat of ethanol
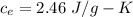
specific heat of aluminium
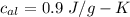
specific heat of ice
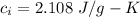
specific heat of water
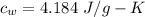
Latent heat of fusion
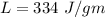
suppose m is the mass of ice added
Heat loss by Al cup and ethanol after
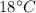 is reached
is reached
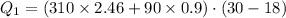
Heat gained by ice such that ice is melted and reached a temperature of
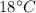
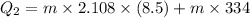
Comparing 1 and 2 we get
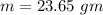
Thus 23.65 gm of ice is added