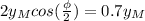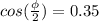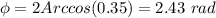Answer:
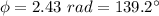
Step-by-step explanation:
The resultant wave of two identical traveling waves of amplitude
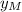 with a phase difference
with a phase difference
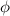 between them is:
between them is:
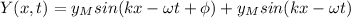
Using the trigonometric formula
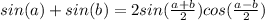
we have:
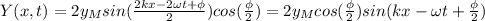
where we can see that the amplitude of the combined wave is
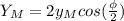 , which we want to be equal to
, which we want to be equal to
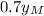 , so we do:
, so we do: