Answer:
a) Our random variable X="number of tests taken until the individual passes" follows a geomteric distribution with probability of success p=0.25
For this case the probability mass function would be given by:
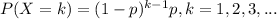
b)
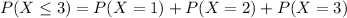
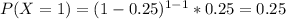
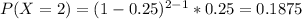
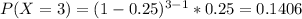
And adding the values we got:
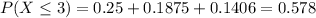
c)
![P(X \geq 5) = 1-P(X<5) = 1- P(X\leq 4)= 1-[P(X=1) +P(X=2) +P(X=3) +P(X=4)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/blu6hmzxv3dmkywun3uuatszypkl08brrd.png)
And we can find the individual probabilities:
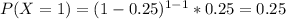
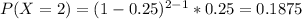
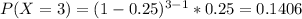
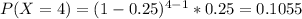
![P(X \geq 5) = 1-[0.25+0.1875+0.1406+0.1055]= 0.316](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/jck0ou748zm1l5linpci9jks2vqtnxxi24.png)
Explanation:
Previous concepts
The geometric distribution represents "the number of failures before you get a success in a series of Bernoulli trials. This discrete probability distribution is represented by the probability density function:"
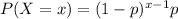
Let X the random variable that measures the number of trials until the first success, we know that X follows this distribution:
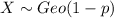
Part a
Our random variable X="number of tests taken until the individual passes" follows a geomteric distribution with probability of success p=0.25
For this case the probability mass function would be given by:
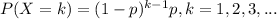
Part b
We want this probability:
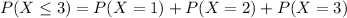
We find the individual probabilities like this:
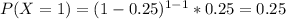
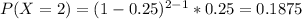
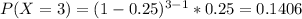
And adding the values we got:
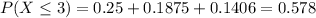
Part c
For this case we want this probability:
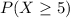
And we can use the complement rule like this:
![P(X \geq 5) = 1-P(X<5) = 1- P(X\leq 4)= 1-[P(X=1) +P(X=2) +P(X=3) +P(X=4)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/blu6hmzxv3dmkywun3uuatszypkl08brrd.png)
And we can find the individual probabilities:
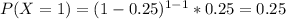
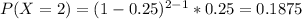
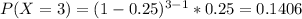
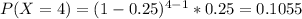
![P(X \geq 5) = 1-[0.25+0.1875+0.1406+0.1055]= 0.316](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/jck0ou748zm1l5linpci9jks2vqtnxxi24.png)