Answer : The value of
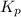 for this reaction is,
for this reaction is,

Explanation :
The given chemical reaction is:

Now we have to calculate value of
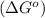 .
.
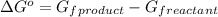
![\Delta G^o=[n_(C_2H_6(g))* \Delta G^0_((C_2H_6(g)))]-[n_(C_2H_2(g))* \Delta G^0_((C_2H_2(g)))+n_(H_2(g))* \Delta G^0_((H_2(g)))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/tz143m5bxg38ey14j81fuucequn52oooy9.png)
where,
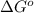 = Gibbs free energy of reaction = ?
= Gibbs free energy of reaction = ?
n = number of moles
 = -32.89 kJ/mol
= -32.89 kJ/mol
 = 209.2 kJ/mol
= 209.2 kJ/mol
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get:
![\Delta G^o=[1mole* (-32.89kJ/mol)]-[1mole* (209.2kJ/mol)+2mole* (0kJ/mol)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/9ptggt3xafxppm71xc0qee3xtfuli1q2kn.png)

The relation between the equilibrium constant and standard Gibbs, free energy is:

where,
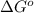 = standard Gibbs, free energy
= standard Gibbs, free energy
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/L.atm
T = temperature = 298 K
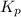 = equilibrium constant = ?
= equilibrium constant = ?
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get:


Thus, the value of
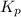 for this reaction is,
for this reaction is,
