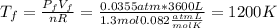Answer:
a)
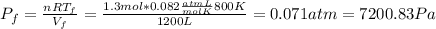
b)
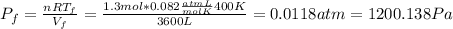
c)
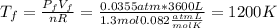
Step-by-step explanation:
a) Consider 1.3 moles of an ideal gas at an initial temperature of 400 K and in a 1.2 m3 closed container. If the gas goes through an isochoric process to twice the initial temperature, what is the new pressure of the gas in Pa?
For this case we have the initial conditions given:
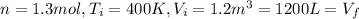
The volume not changes since we have an isochoric process.
For this case we know that the final temperature would be
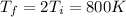 ,
,
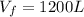 n = 1.3 mol and we can find the final pressure like this:
n = 1.3 mol and we can find the final pressure like this:
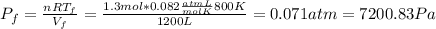
b) Consider 1.3 moles of an ideal gas at an initial temperature of 400 K and in a 1.2 m3closed container. If the gas goes through an isothermal process to 3.6 m3, what is the new pressure of the gas in Pa?
For this case we have the following info:
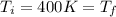 since the process is isothermal
since the process is isothermal
n = 1.3 mol
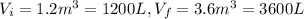
From the ideal gas law we have:
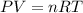
And if solve for the final pressure we got:
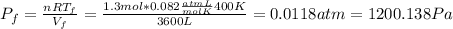
c) Consider 1.3 moles of an ideal gas at an initial temperature of 400 K and in a 1.2 m3 closed container. If the gas goes through an isobaric process to 3.6 m3, what is the new temperature of the gas in Kelvin?
For this case we have the following info:
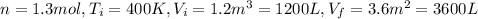
From the initial condition we can find the initial pressure using the ideal gas law:
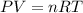
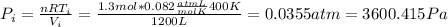
And we know that the pressure not change since the process is isobaric so then
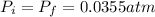 and we can find the final temperature like this:
and we can find the final temperature like this: