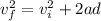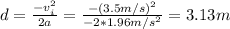Answer:
a)
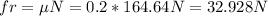
And we need a force
![F> 32.928 N[tex]</p><p>b) [tex] d = (-v^2_i)/(2a)= (-(3.5m/s)^2)/(-2*1.96 m/s^2)= 3.13m](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/5wxlggb6qks1rh0g7n39naruwsxzynmyic.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
Part a
For this case we have the following forces illustrated on the figure attached.
If we analyze on the x axis we just have two forces, fr the friction force and F the force to mantain the movement.
So we need this condition to satisfy the movement:
If we analyze the forces on the y axis we have this:
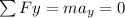
Because we have constant speed for this reason the acceleration is 0
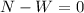
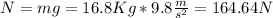
And by definition the friction force is defined as:
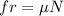
So then the friction force would be:
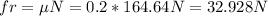
And we need a force
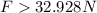
Part b
For this case we assume that F =0 and we have a friction force of 32.928 N.
From the second law of Newton we have:
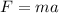
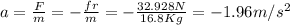
vf =0 (final velocity, rest at the end) and vi = 3.5 m/s.
And we can find the time for the motion like this:
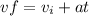
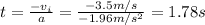
And then we can find the distance from the following formula: