Answer: The partial pressure of oxygen gas is 2.76 bar
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation given by ideal gas which follows:
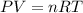
where,
P = pressure of the gas = 5.57 bar
V = Volume of the gas = 2.19 L
T = Temperature of the gas = 298 K
R = Gas constant =
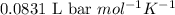
n = Total number of moles = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
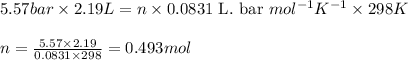
To calculate the mole fraction of carbon dioxide, we use the equation given by Raoult's law, which is:
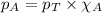 ........(1)
........(1)
where,
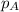 = partial pressure of carbon dioxide = 0.318 bar
= partial pressure of carbon dioxide = 0.318 bar
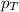 = total pressure = 5.57 bar
= total pressure = 5.57 bar
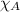 = mole fraction of carbon dioxide = ?
= mole fraction of carbon dioxide = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
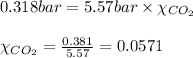
- Mole fraction of a substance is given by:
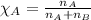
We are given:
Moles of nitrogen gas = 0.221 moles
Mole fraction of nitrogen gas,
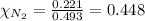
Calculating the partial pressure of oxygen gas by using equation 1, we get:
Mole fraction of oxygen gas = (1 - 0.0571 - 0.448) = 0.4949
Total pressure of the system = 5.57 bar
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
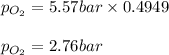
Hence, the partial pressure of oxygen gas is 2.76 bar