Answer:
6
Explanation:
A right Riemann sum approximates a definite integral as:
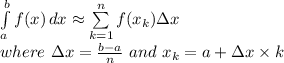
The exact value of the definite integral can be found by taking the limit of the Riemann sum as n approaches infinity:
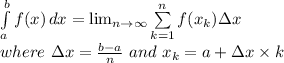
Given that the sum is equal to 2 (n + 1) (3n + 2) / n², the exact value of the integral is:
lim(n→∞) 2 (n + 1) (3n + 2) / n²
lim(n→∞) 2 (3n² + 5n + 2) / n²
lim(n→∞) (6n² + 10n + 4) / n²
6