Answer:
![(f + g)(x) = - 10 \sqrt[3]{2x} \: \: \: (f + g)( - 4) = 20](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/ay5lq52vschmcti3b8jpxtguvb3be9j9v5.png)
![(f - g)(x) =12 \sqrt[3]{2x} \: \: \: (f - g)( - 4) = - 24](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/2no0exh7gn9jl581ty96e9tnm2r6bsipn8.png)
The domain of (f+g)(x) is all real numbers.
The domain of (f-g)(x) is all real numbers.
Explanation:
The given functions are
![f(x) = \sqrt[3]{2x}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/ekh8gtwu03wyl3hp59cftg95z8a4hdaj44.png)
and
![g(x) =- 11\sqrt[3]{2x}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/gm2f0rvub70rfjmobli9k874xrlqr66jl4.png)
By the algebraic properties of polynomial functions:
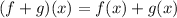
![(f + g)(x) = \sqrt[3]{2x} + - 11 \sqrt[3]{2x}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/4ijbbnk8rgba3gx1rpt1h6lcwmz3nu6p98.png)
This becomes:
![(f + g)(x) = \sqrt[3]{2x} - 11 \sqrt[3]{2x}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/ii5nq7550wrka3p9k5sl29gvar829xi0zx.png)
We subtract to obtain:
![(f + g)(x) = - 10 \sqrt[3]{2x}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/ej7bo3arbdo0hysdjyt3p46i73ui42gnjf.png)
Also
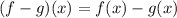
![(f - g)(x) = \sqrt[3]{2x} - - 11 \sqrt[3]{2x}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/c3r335ph0mgz1jtp796dxmzvrvq2cl4h2s.png)
![(f - g)(x) = \sqrt[3]{2x} + 11 \sqrt[3]{2x}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/j3tjnoysrmqn90wmi8y6dqzfsn9qfl4a6f.png)
![(f - g)(x) = 12\sqrt[3]{2x}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/ip6ewmevzfebgzrhwk15upabfqazhkkjxx.png)
When x=-4
![(f + g)( - 4) = - 10\sqrt[3]{2 * - 4}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/lpbnuqi4bfp0cpyw21auxwtbbzlw6e4gf3.png)
![(f + g)( - 4) = - 10\sqrt[3]{ - 8}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/e6hasfm51lzwe0nt8r9byrms9vjo6n3ca8.png)
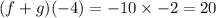
Then also;
![(f - g)( - 4) = 12\sqrt[3]{ - 8}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/4nsqih4wyavtyi24eroyp91brfbwszcnll.png)
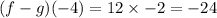
The domain refers to the values that makes the function defined.
Both are cube root functions and are defined for all real numbers.
The domain of (f+g)(x) is all real numbers.
The domain of (f-g)(x) is all real numbers.