Answer: The vapor pressure of a mixture of 80 g of ethanol and 97 g of methanol at 293 K is 78.3 torr.
Step-by-step explanation:
According to Raoult's law, the vapor pressure of a component at a given temperature is equal to the mole fraction of that component multiplied by the vapor pressure of that component in the pure state.
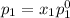 and
and
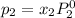
where, x = mole fraction in solution
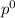 = pressure in the pure state
= pressure in the pure state
According to Dalton's law, the total pressure is the sum of individual pressures.
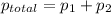
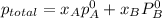
moles of ethanol=
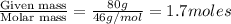
moles of methanol=
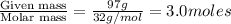
Total moles = moles of ethanol + moles of methanol = 1.7 +3.0 = 4.7
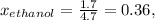
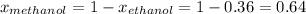
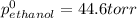
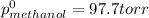
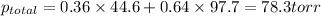
Thus the vapor pressure of a mixture of 80 g of ethanol and 97 g of methanol at 293 K is 78.3 torr.