Answer:
series: Voc = 1.2V, JL =
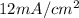
parallel: Voc = 0.5V, JL =
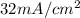
Step-by-step explanation:
In series connection,
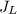 is minimum of all current densities of all cells in series therefore current density or short circuit current will be
is minimum of all current densities of all cells in series therefore current density or short circuit current will be
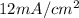 .
.
And open circuit voltage will be the sum of two voltages = 0.5+0.7 = 1.2V
I-V graph of two series solar cells is attached here as first image
In parallel connection, there is same voltage across all cells. So voltage across all cells will be the minimum voltages of all cells i.e 0.5V.
And resulting current will be the sum of all currents i.e 12 + 20 =
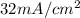 .
.
I-V characteristic of parallel connection of solar cells is attached as second image.