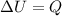Answer:
C. Equals the sum of all forms of energy contained within the system.
D. Equals the heat entering the system at constant volume.
E. Equals the heat entering the system plus the work done on the system
Step-by-step explanation:
Internal energy is defined as the sum of internal kinetic energy and internal potential energy, that is, the energy contained within the system.
The first law of thermodynamics relates the change in the internal energy with the heat entering the system (Q) and work done on the system (W), with the following expression:
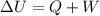
If the system is at constant volume the work done is zero. Therefore, the heat entering the system increases its internal energy: