Step-by-step explanation:
It is known that,
Molar mass of Cd = 112.41 g/mol
Standard concentration of Cd = 0.005 mg/L =
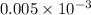 g/L
g/L
Hence, we will calculate the molarity as follows.
Molarity =
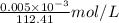
=
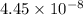 M
M
Equation for the reaction is as follows.
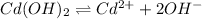
![K_(sp) = [Cd^(2+)][OH^(-)]^(2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/3tjwcbxdclgmzlgr4p2m2pk848cpg3hihl.png)
![2 * 10^(-34) = 4.45 * 10^(-8) * [OH^(-)]^(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/evukqbxaobhlwxvzn8gkrq5l0dtmdg1hqn.png)
![[OH^(-)] = 6.7 * 10^(-4)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/qu0c7v1augnyunvtkpq3qke6ft2yhj54qb.png) M
M
Also,
![[H^(+)] = (10^(-14))/([OH^(-)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/u2jitzuorrzgnw1c2tbo4vsxgphmbszrsi.png)
=
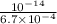
=
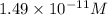
Relation between pH and concentration of hydrogen ions is as follows.
pH =
![-log [H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/hggt6ye9u4ukk181i3mah9cn5ybt9okq1d.png)
=
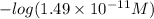
= 10.82
Thus, we can conclude that a minimum pH of 10.82 is necessary to reduce the dissolved cadmium ion concentration to the standard.