The given question is incomplete. The complete question is as follows.
A certain liquid has a normal boiling point of
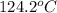 and a boiling point elevation constant
and a boiling point elevation constant
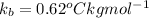 . A solution is prepared by dissolving some sodium chloride (NaCl) in 6.50 g of X. This solution boils at
. A solution is prepared by dissolving some sodium chloride (NaCl) in 6.50 g of X. This solution boils at
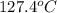 . Calculate the mass of NaCl that was dissolved. Round your answer to significant digits.
. Calculate the mass of NaCl that was dissolved. Round your answer to significant digits.
Step-by-step explanation:
As per the colligative property, the elevation in boiling point will be as follows.
T = boiling point of the solution =
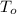 = boiling point of the pure solvent =
= boiling point of the pure solvent =
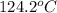
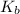 = elevation of boiling constant =
= elevation of boiling constant =
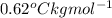
We will calculate the molality as follows.
molality =
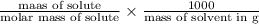
i = vant hoff's factor
As NaCl is soluble in water and dissociates into sodium and chlorine ions so i = 2.
Putting the given values into the above formula as follows.
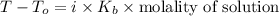
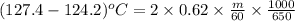
m = 100 g
Therefore, we can conclude that 100 g of NaCl was dissolved.