Answer:
1751399.8902 J
Step-by-step explanation:
m = Mass of water = 74.6 kg
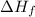 = Latent heat of fusion =
= Latent heat of fusion =
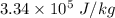
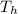 = 19.2°C
= 19.2°C
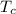 = 0°C
= 0°C
We have the equation for cold body
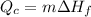
We have the equation
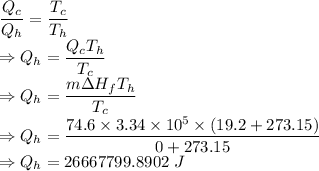
Energy rejected to the room is 26667799.8902 J
Energy supplied to the device is given by
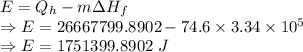
The energy supplied to the device is 1751399.8902 J