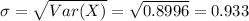Answer:
a) X 1 2 3 4 5
P(X) 0.7 0.15 0.10 0.03 0.02
b)
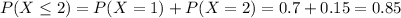
c)
![P(X >3) = 1-P(X \leq 3) = 1-[P(X=1) +P(X=2)+P(X=3)]=1-[0.7+0.15+0.1]= 0.05](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/qx13a1x9ehxhbkzufbhf0vt0o77oqyr0sf.png)
d)
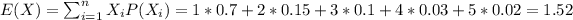
e)
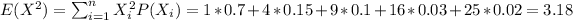
![Var(X) = E(X^2) -[E(X)]^2= 3.18- (1.52)^2 = 0.8996](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/9hz5ovpv15ie88k26jmtax46swsew8zbgo.png)
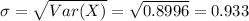
Explanation:
Part a
From the information given we define the probability distribution like this:
X 1 2 3 4 5
P(X) 0.7 0.15 0.10 0.03 0.02
And we see that the sum of the probabilities is 1 so then we have a probability distribution
Part b
We want to find this probability:
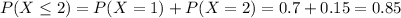
Part c
We want to find this probability
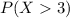
And for this case we can use the complement rule and we got:
![P(X >3) = 1-P(X \leq 3) = 1-[P(X=1) +P(X=2)+P(X=3)]=1-[0.7+0.15+0.1]= 0.05](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/qx13a1x9ehxhbkzufbhf0vt0o77oqyr0sf.png)
Part d
We can find the expected value with this formula:
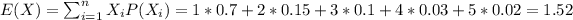
Part e
For this case we need to find first the second moment given by:
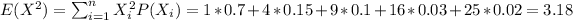
And we can find the variance with the following formula:
![Var(X) = E(X^2) -[E(X)]^2= 3.18- (1.52)^2 = 0.8996](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/9hz5ovpv15ie88k26jmtax46swsew8zbgo.png)
And we can find the deviation taking the square root of the variance: