Answer:
(a). The potential is 78.0 kV.
(b). The potential is zero.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Radius = 6.00
Charge density = 8.50 μC/m
(a). The surface of the cylinder and 4.00 cm away from the surface,
We need to calculate the voltage
Using formula of potential
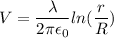
Put the value into the formula
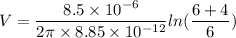
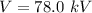
(b). The surface and a point 1.00 cm from the central axis of the cylinder
Here, r = R
We need to calculate the voltage
Using formula of potential
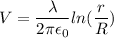
Put the value into the formula
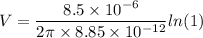
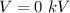
Hence, (a). The potential is 78.0 kV.
(b). The potential is zero.