Answer:
Null Hypothesis is rejected that concluded that mean science test score is lower for students taught in traditional lab sessions than it is for students taught using interactive simulation software.
Explanation:
We are given that two teaching methods and their effects on science test scores are being reviewed.
Also,
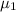 = mean test score for the students taught in traditional lab sessions.
= mean test score for the students taught in traditional lab sessions.
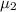 = mean test score for students taught using interactive simulation
= mean test score for students taught using interactive simulation
software.
Null Hypothesis,
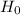 :
:
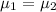 {Both traditional lab sessions and interactive
{Both traditional lab sessions and interactive
simulation software has same mean test score}
Alternate Hypothesis,
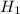 :
:
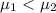 {Students taught in traditional lab sessions has lower mean science test score than students taught using interactive simulation software}
{Students taught in traditional lab sessions has lower mean science test score than students taught using interactive simulation software}
The test statistics we use here will be :
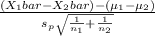 follows
follows
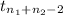
where,
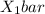 = 76.1 and
= 76.1 and
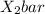 = 87.1
= 87.1
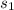 = 4.4 and
= 4.4 and
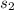 = 5.8
= 5.8
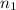 = 46 and
= 46 and
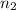 = 46
= 46
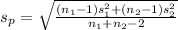 =
=
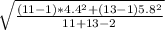 = 5.210
= 5.210
Here, we use t test statistics because we know nothing about population standard deviations.
Test statistics =
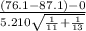 follows
follows
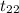
= -5.154
At 0.05 or 5% level of significance t table gives a critical value of -1.717 at 22 degree of freedom. Since our test statistics is less than the critical table value of t as -5.154 < -1.717 so we have sufficient evidence to reject null hypothesis as it will fall in the rejection region.
Therefore, we conclude that mean science test score is lower for students taught in traditional lab sessions than it is for students taught using interactive simulation software.