Answer: 365 K
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the Arrhenius equation,
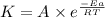
or,
![\log ((K_2)/(K_1))=(Ea)/(2.303* R)[(1)/(T_1)-(1)/(T_2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/x29hmr496eckje089dimzyhsspavwcfh8n.png)
where,
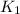 = rate constant at
= rate constant at
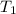 = 1.00
= 1.00
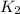 = rate constant at
= rate constant at
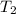 = 5.00
= 5.00
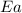 = activation energy for the reaction = 28.90 kJ/mol= 28900 j/mol
= activation energy for the reaction = 28.90 kJ/mol= 28900 j/mol
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/mole.K
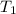 = initial temperature = 313 K
= initial temperature = 313 K
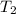 = final temperature = ?
= final temperature = ?
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get
![\log ((5.00)/(1.00))=(28900)/(2.303* 8.314J/mole.K)[(1)/(313K)-(1)/(T_2K)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/dp2f4tidnfnc0zz0o3feg2nuj3znkqewlg.png)
![0.69=(28900)/(2.303* 8.314J/mole.K)[(1)/(313K)-(1)/(T_2K)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/9x3zrxwm0lntg5ja4zzvlx5vjrb8csc6f9.png)
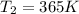
Therefore, 365 K is required to increase the reaction rate by 5.00 times.