Answer:
The answer to the question is 0.0122 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
The rate of a reaction is the measure of the change in concentration of a reagent within a specific time frame. Reaction rate of a substance can be calculated by finding the division of the concentration change of the substance and the time required to undergo the change in concentration.
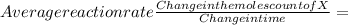
The initial number of moles of X = 0.732 moles and final number of moles of X = 0 moles and the time it took to effect the change = 60s
then the rate of reaction =
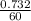 = 0. 0122 moles per second
= 0. 0122 moles per second
the rate of the reaction involving X = 0.0122 m/s