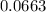Answer:
Part A :
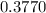
Part B :
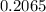
Part C :
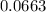
Explanation:
Let's start defining the random variable.
If X : ''Time between arrivals of customers at a store'' is the exponential random variable, its probability distribution function will be :
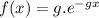
Where
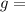 λ is the parameter of the exponential distribution.
λ is the parameter of the exponential distribution.
Also λ = 1 / μ where μ is the mean of the distribution.
Using the data of the exercise :
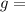 λ =
λ =
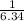
The cumulative distribution function of the exponential random variable is :
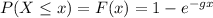
For this exercise :
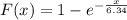 (I)
(I)
We are going to use the equation (I) to calculate all the probabilities.
Part A :
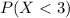
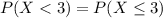 because the exponential distribution is a continuous random variable ⇒
because the exponential distribution is a continuous random variable ⇒
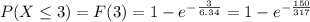 ≅
≅
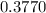
Part B :
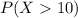 ⇒
⇒
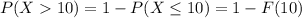 ⇒
⇒
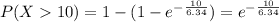 ≅
≅
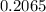
Part C :
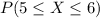 ⇒
⇒
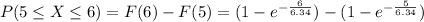 ⇒
⇒
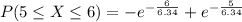 ≅
≅