Answer:
The force on q₁ due to q₂ is (0.00973i + 0.02798j) N
Step-by-step explanation:
F₂₁ =
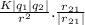
Where;
F₂₁ is the vector force on q₁ due to q₂
K is the coulomb's constant = 8.99 X 10⁹ Nm²/C²
r₂₁ is the unit vector
|r₂₁| is the magnitude of the unit vector
|q₁| is the absolute charge on point charge one
|q₂| is the absolute charge on point charge two
r₂₁ = [(9-5)i +(7.4-(-4))j] = (4i + 11.5j)
|r₂₁| =
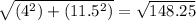
(|r₂₁|)² = 148.25
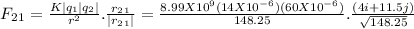
= 0.050938(0.19107i + 0.54933j) N
= (0.00973i + 0.02798j) N
Therefore, the force on q₁ due to q₂ is (0.00973i + 0.02798j) N