Answer:
g = 1.11x10⁻⁵Ω.
Step-by-step explanation:
The membrane conductance (g) can be calculated by dividing membrane current (I) through the driving force (Vm - E) as follows:
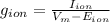
where Vm: is the membrane potential and
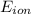 : is the equilibrium potential for the ion or reversal potential.
: is the equilibrium potential for the ion or reversal potential.
The equilibrium potential for the ion can be calculated using the Nernst equation:
![E_(ion) = (RT)/(zF)*Ln(([ion]_(out))/([ion]_(ins)))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/i7uajh2aihs8a7aasfa6d9zum5xbjamb8m.png)
where R: is the gas constant = 8.314 J/K*mol, F: is the Faraday constant = 96500 C/mol, T: is the temperature (K), z: is the ion's charge, [ion]out and [ion]ins: is the concentration of the ion outside and inside, respectively.
![E_(ion) = ((8.314 J*K^(-1)*mol^(-1))((15 + 273)K))/((+1)(96500 C*mol^(-1)))*Ln(([500mM])/([70mM])) = 48.78 mV](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/nelfnze42t8nqe0zy8a34nx1265zp20qcg.png)
Now, we can calculate the membrane conductance (g) using equation (1):
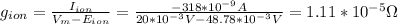
Therefore, the membrane conductance is 1.11x10⁻⁵Ω.
I hope it helps you!