Answer: The precipitate will not be formed in the above solution.
Step-by-step explanation:
The chemical equation for the reaction of potassium bromide and lead acetate follows:
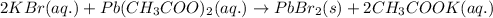
We are given:
Concentration of KBr = 0.013 M
Concentration of lead acetate = 0.0035 M
1 mole of KBr produces 1 mole of potassium ions and 1 mole of bromide ions
So, concentration of bromide ions = 0.013 M
1 mole of lead (II) acetate produces 1 mole of lead (II) ions and 2 moles of acetate ions
So, concentration of lead (II) ions = 0.0035 M
The salt produced is lead (II) bromide
The equation follows:
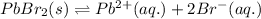
The expression of
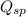 for above equation follows:
for above equation follows:
![Q_(sp)=[Pb^(2+)]* [Br^-]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/6oon5vddt4bnm5rpzssqfnr91xn2gubrso.png)
Putting values of the concentrations in above expression, we get:
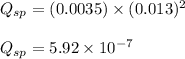
We know that:
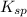 for lead (II) bromide =
for lead (II) bromide =
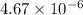
There are 3 conditions:
- When
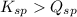 ; the reaction is product favored. (No precipitation)
; the reaction is product favored. (No precipitation) - When
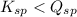 ; the reaction is reactant favored. (Precipitation occurs)
; the reaction is reactant favored. (Precipitation occurs) - When
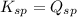 ; the reaction is in equilibrium. (sparingly soluble)
; the reaction is in equilibrium. (sparingly soluble)
As, the
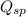 is less than
is less than
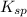 . The above reaction is product favored. This means that no salt or precipitate will be formed.
. The above reaction is product favored. This means that no salt or precipitate will be formed.
Hence, the precipitate will not be formed in the above solution.