Answer:
(A) 0.0625
(B) 25%
Step-by-step explanation:
A
Given that ;
T is tall
t is short
R is red
r is tan.
If a short, tan male goat mates with a tall, red female goat of an unknown genotype;
Let's take it one after the other;
A short tan male goat = ttrr
The female goat is an unknown genotype, we will have to determine that but we were told that it is tall and red
∴ For tall it is T and red is R;
Definitely, the female genotype should be T_ R_;
the probability genotype of the female for each allele is either:
- TT or Tt
- RR or Rr
However, from above;
the probability that the female will be Tt =
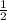
the probability that the female will be Rr =
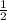
the probability that the recessive allele 't' will be transferred to the offspring =
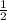
the probability that the recessive allele 'r' will be transferred to the offspring =
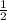
∴ the probability that they would produce short, tan offspring (ttrr) will be;
=
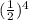
=
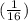
= 0.0625
(B)
One of a pea plants is homozygous recessive for both genes, resulting in the cross Yy Rr × yy rr. Calculate the percentage of green and round offspring.
For Color, Let;
Y = Yellow
y = Green
For shape, Let;
R = Round
r = wrinkled
If a cross occur between Yy Rr × yy rr. (i.e yellowround and green wrinkled)
the percentage of green and round offspring will be;
If Yy Rr self crossed; we have the following traits (YR, Yr, yR, yr)
yy rr will result to (yr, yr)
YR Yr yR yr
yr YyRr Yyrr yyRr Yyrr
yr YyRr Yyrr yyRr Yyrr
Yellow Yellow Green Green
Round Wrinkled Round Wrinkled
Therefore, the percentage of Green and Round offsprings from above is:
=
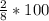 %
%
=
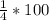 %
%
= 25%