The momentum of the object is 1500 kgm/s.
Step-by-step explanation:
The law of conservation of momentum states that without effect of any external force in the system, the momentum of the system remains conserved. And momentum is defined as the product of the mass and velocity of the object.
Here, the mass of the 1st body = 200kg.
The mass of the 2nd body = 150kg.
Velocity of the 1st body = 15 m/s.
Velocity of the 2nd body = - 10 m/s.
So, the total momentum of the system before collision =
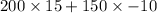 kgm/s
kgm/s
= 1500 kgm/s.
After the collision, the body sticks together.
So, the total mass =200+150 kg = 350 kg.
Momentum remains conserved. So the momentum of the body= 1500 kgm/s.