Step-by-step explanation:
(a) The given data is as follows.
Temperature (T) =
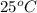 = (25 + 273) K = 298 K
= (25 + 273) K = 298 K
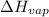 = 43000 J/mol
= 43000 J/mol
Since, both the liquid and vapors are at equilibrium. Therefore, change in free energy will be calculated as follows.
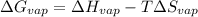 = 0
= 0
43000 -
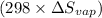 = 0
= 0
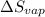 = -144 J/mol K
= -144 J/mol K
Negative sign indicates an increase in entropy of the system.
Now, for 1 mole of
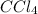 is as follows.
is as follows.
= 144 J/K
So,
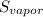 - 214 = 144 J/k
- 214 = 144 J/k
= 358 J/K
Therefore, we can conclude that entropy of
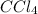 vapor is 358 J/K.
vapor is 358 J/K.
(b) As we know that intensive variable are the variables which do not depend on the amount of a substance.
So, in the given situation only temperature will act as an intensive variable that will be required to completely specify the vapor-liquid mixture of
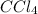 .
.