Answer:
Explanation below.
Explanation:
For this case we have the following dataset:
46, 16, 41, 26, 22 ,33, 30, 22 ,36, 34,
63, 21, 26, 18, 27, 24, 31, 38, 26, 55,
31, 47, 27, 43 ,35, 22 ,64,40, 58, 20,
49, 37, 53, 25, 29, 32, 23, 49, 39, 40,
24, 56, 30, 51, 21, 45, 27, 34, 47, 35
So we have 50 values. The first step on this case would be order the dataset on increasing way and we got:
16, 18, 20, 21, 21, 22, 22, 22, 23, 24,
24, 25, 26, 26, 26, 27, 27, 27, 29, 30
30, 31, 31, 32, 33, 34, 34, 35, 35, 36,
37, 38, 39, 40, 40, 41, 43, 45, 46, 47,
47, 49, 49, 51, 53, 55, 56, 58, 63, 64
We can find the range for this dataset like this:
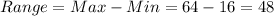
Then since we need 7 classes we can find the length for each class doing this:
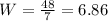
And now we can define the classes like this and counting how many observations lies on each interval we got the frequency:
Class Frequency Midpoint RF CF
________________________________________________
[16-22.86) 8 19.43 (8/50)=0.16 0.16
[22.86-29.71) 11 26.29 (11/50)=0.22 0.38
[29.71-36.57) 11 33.14 (11/50)=0.22 0.6
[36.57-43.43) 7 40.0 (7/50)=0.14 0.74
[43.43-50.29) 6 46.86 (6/50)=0.12 0.86
[50.29-57.14) 4 53.72 (4/50)=0.08 0.94
[57.14-64] 3 60.57 (3/50)=0.06 1.0
________________________________________________
Total 50 1.00
RF= Relative frequency. CF= Cumulative frequency
The relative frequency was calculated as the individual frequency for a class divided by the total of observations (50)
The mid point is the average between the limits of the class.
And the cumulative frequency is calculated adding the relative frequencies for each class.