Answer:
0.009 moles
Step-by-step explanation:
Using integrated rate law for first order kinetics as:
![[A_t]=[A_0]e^(-kt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/p2vpxs9cve2w798wzy926mzqzvfv5si8xr.png)
Where,
![[A_t]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/c6se0yk0a5jz0ud2m1a9jh5tv0rk9jx59i.png) is the concentration at time t
is the concentration at time t
![[A_0]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/i49y9xugeve1tuhjmf05tpufcmfey5f0yu.png) is the initial concentration
is the initial concentration
Given that:
The rate constant, k =
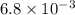 s⁻¹
s⁻¹
Initial concentration
![[A_0]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/i49y9xugeve1tuhjmf05tpufcmfey5f0yu.png) = 0.0250 mol
= 0.0250 mol
Final concentration
![[A_t]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/c6se0yk0a5jz0ud2m1a9jh5tv0rk9jx59i.png) = ?
= ?
Time = 2.5 min = 2.5 x 60 seconds = 150 sec
Applying in the above equation, we get that:-
![[A_t]=0.0250e^{-6.8* 10^(-3)* 150}\ moles=0.025* \frac{1}{e^{(51)/(50)}}\ moles=(0.025)/(2.77319)\ moles=0.009\ moles](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ozgwgtry2vk1bun81k2dc2tbf3hsdnbd32.png)