Answer: The molar mass of the unknown protein is 6387.9 g/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the concentration of solute, we use the equation for osmotic pressure, which is:
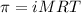
or,
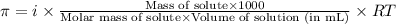
where,
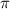 = osmotic pressure of the solution = 0.0766 atm
= osmotic pressure of the solution = 0.0766 atm
i = Van't hoff factor = 1 (for non-electrolytes)
Mass of protein = 100. mg = 0.100 g (Conversion factor: 1 g = 1000 mg)
Molar mass of protein = ?
Volume of solution = 5.00 mL
R = Gas constant =
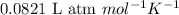
T = temperature of the solution =
![25^oC=[25+273]K=298K](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/h90rloyf77jo1jed7el4n760wq4iuiuecg.png)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
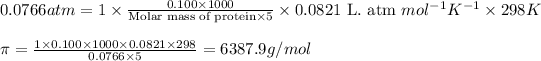
Hence, the molar mass of the unknown protein is 6387.9 g/mol