Answer: The
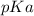 of the acid is 6.09
of the acid is 6.09
Step-by-step explanation:
For the given chemical reaction:
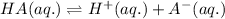
The expression of equilibrium constant [tex[(K_a)[/tex] for the above equation follows:
![K_a=([H^+][A^-])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/cd33ttbdpkk5h562zi8dnbyn0akiej88j5.png)
We are given:
![[HA]_(eq)=0.200M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/gpp51p6nvykqo0s6glfrjdlnweam3nhyey.png)
![[H^+]_(eq)=4.00* 10^(-4)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/axt73f1l45pieeq6fbvjhpa524spkczlwa.png)
![[A^-]_(eq)=4.00* 10^(-4)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ds024gqz1bl2dfti8knvygdk7153ktn79d.png)
Putting values in above expression, we get:
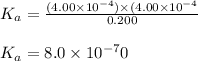
p-function is defined as the negative logarithm of any concentration.
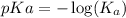
So,
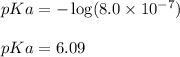
Hence, the
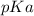 of the acid is 6.09
of the acid is 6.09