Answer:
The correct answer is
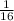 or zero, depending on the fathers genotype.
or zero, depending on the fathers genotype.
Step-by-step explanation:
- According to the question,
- dark hair phenotype is dominant over light hair.
- freckled phenotype is dominant over non-freckled phenotype.
- Let for hairs, dominant allele be D and the recessive allele be d.
- Let for freckles, dominant allele be F and the recessive allele be f.
- According to the question, the mother is heterozygous for both the traits, that is, she has the genotype, DdFf and phenotype, dark hair and freckles.
- But the father is said to have the same traits but not mentioned to be homozygous (DDFF) or heterozygous (DdFf).
- If he is homozygous, then he would produce only DF gametes.
- The mother produces the following gametes : DF, Df, dF, df.
- On crossing homozygous father (DDFF) with heterozygous mother (DdFf), all the offspring will have dark hair with freckles, so probability of obtaining a child with light hair and no freckles is zero.
- If both the parents are heterozygous, DdFf,
- Crossing them,
DF Df dF df
DF DDFF DDFf DdFF DdFf
(D/F) (D/F) (D/F) (D/F)
Df DDFf DDff DdFf Ddff
(D/F) (D/NF) (D/F) (D/NF)
dF DdFF DdFf ddFF ddFf
(D/F) (D/F) (L/F) (L/F)
df DdFf Ddff ddFf ddff
(D/F) (D/NF) (L/F) (L/NF)
- In the above cross, in the brackets (),
- D means dark hair.
- F means freckled.
- L means light hair.
- NF means non-freckled.
- The phenotypes observed are :
- Dark hair with freckled - 9.
- Dark hair with non-freckled - 3.
- Light hair with freckled -3.
- Light hair with non-freckled - 1.
- Probability that a child born would be light haired with no freckles (ddff) is
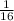 .
.