Answer:
the equation
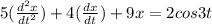 is a partial differential equation(PDE) because it contains unknown multi variables and their derivatives. This is a PDE of order 2.
is a partial differential equation(PDE) because it contains unknown multi variables and their derivatives. This is a PDE of order 2.
The independent variable is x while the dependent variable is t.
The PDE is Linear.
Explanation:
Partial Differential Equation (PDE): This is a differential equation that contains multi variables and their derivatives.
Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE): this is a differential equation containing a function of one independent variable and its derivatives.