Answer:
The air molecules that are surrounding the metal will speed up, and the molecules in the metal will slow down.
Step-by-step explanation:
The hot metal at 150 °C loses heat energy by conduction to the surrounding air molecukes and as such cools down, the cooler metal consists of lesser enery to power the movement of the molecules of the metal hence the metal molecules slows down in their movement as seen in the equation of heat and temperature
ΔH = m×C×ΔT where ΔH is the change in heat energy (heat loss of the metal, C is the heat capacity and ΔT is the temperature change
For the surrounding air that experiences increase in temperature the same process follows leading to increase in the kinetic energy of the air molecules and decrease in kinetic energy of the metal molecules as shown in the formula
K =
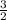 ×
×
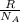 ×T where K = Kinetic Energy, R = gas constant (8.314J/mol×K) and
×T where K = Kinetic Energy, R = gas constant (8.314J/mol×K) and
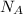 = Avogadros number (6.022×
= Avogadros number (6.022×
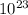 atoms/mol)
atoms/mol)