Answer:
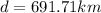
Step-by-step explanation:
The time lag between the arrival of transverse waves and the arrival of the longitudinal waves is defined as:
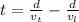
Here d is the distance at which the earthquake take place and
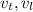 is the velocity of the transverse waves and longitudinal waves respectively. Solving for d:
is the velocity of the transverse waves and longitudinal waves respectively. Solving for d:
