Answer:
(3, 0) and (5, 0)
Explanation:
we have
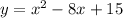
we know that
The x-intercepts are the values of x when the value of y is equal to zero
so
For y=0
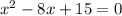
The formula to solve a quadratic equation of the form
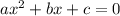
is equal to
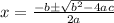
in this problem we have
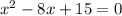
so
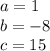
substitute in the formula
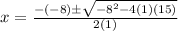
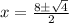
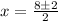
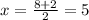
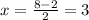
so
x=3, x=5
therefore
The x-intercepts are (3,0) and (5,0)