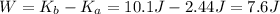Answer:
1) 2.44 joules
2) 7.73 m/s
3) 7.6 joules
Step-by-step explanation:
Kinetic energy (K) of a particle is:
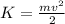 (1)
(1)
with m the mass, and v the velocity
1) Because we already now velocity on A (va) and the mass of the object we can calculate its kinetic energy:
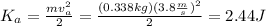
2) Because on B we know mass and kinetic energy we should solve (1) for v and use our values to find the velocity on B:
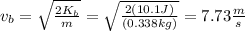
3) Work-energy theorem states that the change of kinetic energy of an object is equal to the total work done on it, so: