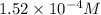Answer: The concentration of
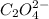 at equilibrium is
at equilibrium is
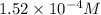
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given:
Molarity of oxalic acid solution = 0.019 M
Oxalic acid
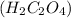 is a weak acid and will dissociate 2 hydrogen ions.
is a weak acid and will dissociate 2 hydrogen ions.
- The chemical equation for the first dissociation of oxalic acid follows:
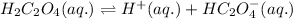
Initial: 0.019
At eqllm: 0.019-x x x
The expression of first equilibrium constant equation follows:
![Ka_1=([H^+][HC_2O_4^(-)])/([H_2C_2O_4])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/9sy4stg63ye737vp2qgv9l1rch7n3z7h3d.png)
We know that:
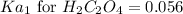
Putting values in above equation, we get:
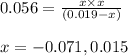
Neglecting the negative value of 'x', because concentration cannot be negative.
- The chemical equation for the second dissociation of oxalic acid:
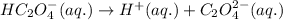
Initial: 0.015
At eqllm: 0.015-y 0.015+y y
The expression of second equilibrium constant equation follows:
![Ka_2=([H^+][C_2O_4^(2-)])/([HC_2O_4^-])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/8ko18cdu9346mwjaj9yl0e9anfqxh24tki.png)
We know that:
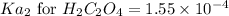
Putting values in above equation, we get:
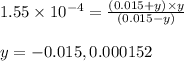
Neglecting the negative value of 'y', because concentration cannot be negative.
So, equilibrium concentration of oxalate ion = y = 0.000152 M
Hence, the concentration of
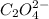 at equilibrium is
at equilibrium is