Answer:
Initial rate of the reaction when concentration of hydrogen gas is doubled will be
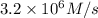 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
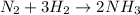
Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
Initial rate of the reaction = R =
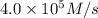
![R = k* [N_2][H_2]^3](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/nscsnqmhdb74gys8cmm5dxzj7q79gmstkt.png)
![4.0* 10^5 M/s=k* [N_2][H_2]^3](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/8xpep0fxg4uwtgtlayv4t7orwlgcb3ghdy.png)
The initial rate of the reaction when concentration of hydrogen gas is doubled : R'
![[H_2]'=2[H_2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/afdkdw8gyujot868x1216nfm4m0qkn4vcv.png)
![R'=k* [N_2][H_2]'^3=k* [N_2][2H_2]^3](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/sqvyums4flrt5jy5p13cg7jwtvzqak93iq.png)
![R'=8* k* [N_2][H_2]^3](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/stveaqr2pellu5bq7uriyevndogvtnd009.png)
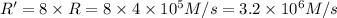
Initial rate of the reaction when concentration of hydrogen gas is doubled will be
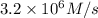 .
.