Answer:
The unknown substance is rhodium.
Step-by-step explanation:
Heat lost by hot substance will be equal to heat gained by the water
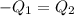
Mass of substance=
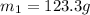
Specific heat capacity of substance=
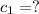
Initial temperature of the substance =
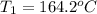
Final temperature of substance=
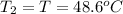
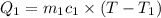
Mass of water = M
Volume of water ,V= 35 ml
Density of water = d = 1.00 g/mL
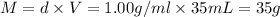
Mass of water=
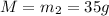
Specific heat capacity of water=
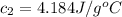
Initial temperature of the water =
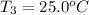
Final temperature of water =
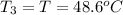
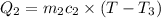
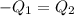
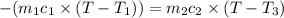
On substituting all values:
we get,
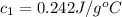
The value of heat capacity of the substance is equal to that of rhodium metal.Hence, the unknown substance is rhodium.