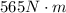To solve this problem we will apply Gauss's law which defines the electric flow as the proportional change of the charge on the vacuum permittivity. Mathematically said this is,
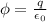
Here,
q = Charge
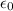 = Vacuum permittivity
= Vacuum permittivity
We will start calculating the load inside the box
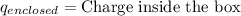

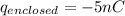
Now if the vacuum permittivity is equivalent to,
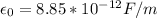
We can replace in our first equation:
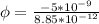
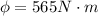
Therefore the electric flux through the surface of the box is