To solve this problem we will apply the relation of Ohm's law, at the same time we will use the concept of resistance in a cable, resistivity and potential difference.
According to Ohm's law we have to
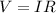
Here,
V = Voltage
I = Current
R = Resistance
At the same time resistance can be described as
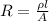
Here,
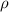 = Resistivity of the material
= Resistivity of the material
l = Length of the specimen
A = Cross-sectional area
From the above expression we can write the current as,
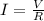
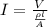
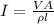
Replacing we have that,
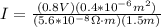
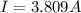
Therefore the current in the wire is 3.809A
Note: The value obtained for the resistivity of Tungsten was theoretically obtained and can be consulted online.