Answer:
Part a: The rate of the equation for 1st order reaction is given as
![Rate=k[H_2O_2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/yi3j9w18r236s749ozxq0b14iexwplnjky.png)
Part b: The integrated Rate Law is given as
![[H_2O_2]=[H_2O_2]_0 e^(-kt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/hv6kjudiicmelyp4txwcrfc5srmvzdbzth.png)
Part c: The value of rate constant is
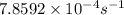
Part d: Concentration after 4000 s is 0.043 M.
Step-by-step explanation:
By plotting the relation between the natural log of concentration of
 , the graph forms a straight line as indicated in the figure attached. This indicates that the reaction is of 1st order.
, the graph forms a straight line as indicated in the figure attached. This indicates that the reaction is of 1st order.
Part a
Rate Law
The rate of the equation for 1st order reaction is given as
![Rate=k[H_2O_2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/yi3j9w18r236s749ozxq0b14iexwplnjky.png)
Part b
Integrated Rate Law
The integrated Rate Law is given as
![[H_2O_2]=[H_2O_2]_0 e^(-kt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/hv6kjudiicmelyp4txwcrfc5srmvzdbzth.png)
Part c
Value of the Rate Constant
Value of the rate constant is given by using the relation between 1st two observations i.e.
t1=0, M1=1.00
t2=120 s , M2=0.91
So k is calculated as
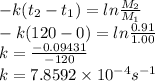
The value of rate constant is
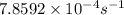
Part d
Concentration after 4000 s is given as
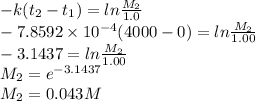
Concentration after 4000 s is 0.043 M.